Posted on
What can be deducted as an extraordinary expense?
Parking, commuting, hospitality, or meal expenses... there are many preconceived ideas about what can be deducted as an extraordinary expense, and it is not always easy to understand. We'll explain you what you can deduct!
1. What is an extraordinary expense?
Extraordinary expenses are "unavoidable" and "substantially reduce the taxpayer's ability to pay". It is an expense that "is not in principle imposed on most taxpayers" and "the taxpayer can't be exempted from it for material, legal or moral reasons."
2. What types of expenses can be deducted?
Expenses considered as extraordinary expenses include:
- Care of ascendants and descendants (parents or children)
- Care of dependents
- Medical expenses not covered by the CNS nor by your health insurance
- Costs of a lawsuit against you (e.g. wrongful dismissal)
- Divorce expenses
- Costs of treatment (with a doctor's prescription)
- Dieting (with a doctor's prescription)
- Dietary plans (with a doctor's prescription)
- Retirement home or nursing home expenses
- Funeral expenses
- Child adoption expenses
3. What are the requirements?
For the deduction of expenses to be accepted, all supporting documents must be attached to prove the amounts incurred by the taxpayer, otherwise the tax authorities will systematically refuse the deduction of expenses.
Moreover, to be considered as extraordinary, an expense must reduce the taxpayer's ability to pay, i.e. have a real impact on the financial situation of the household. This depends of course on the income of each household, which is why an expense could be considered as extraordinary for a modest household and considered as an ordinary expense for a wealthier household. So how do you determine this objectively?
It is the normal expense threshold that determines the amount at which an expense can or cannot be considered extraordinary. It is based on the household's taxable income and family situation (tax class and number of dependent children).
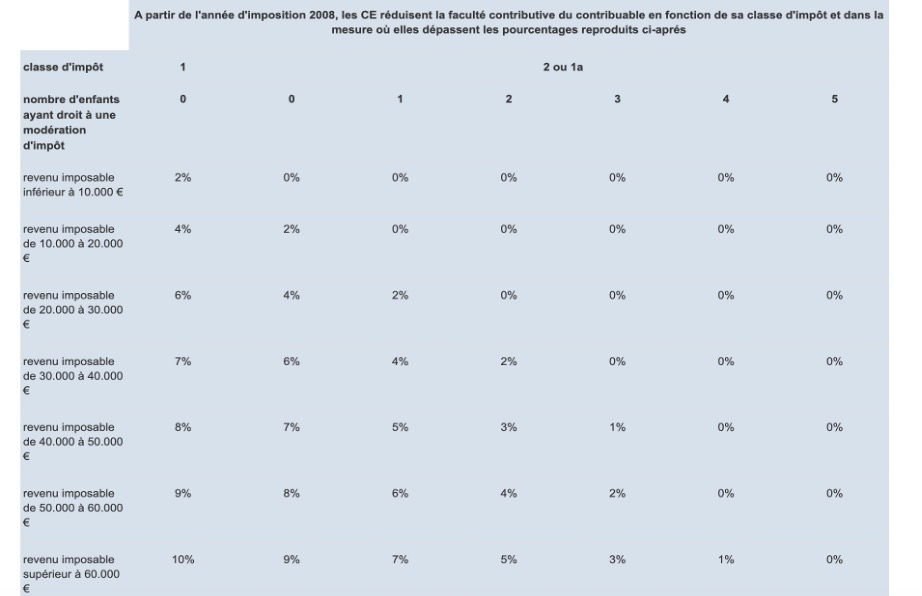
Example 1
Mia is single, without children and has a taxable income of 32,000 euros. She had to pay legal fees during the year because she was victim of poor workmanship during the construction of her apartment. The lawyer's fees amount to 1,700 euros. Can she deduct these costs?
Solution
1. Is it an extraordinary expense?
Yes: Mia suffered a harm for which she was not responsible and could not avoid it.
This is a valid reason to claim the extraordinary expense deduction.
2. The threshold of normal load is determined as follows:
Her normal expense threshold is equal to = 32,000 x 7% = 2,240 euros.
However, Mia has incurred 1,700 euros in expenses, which is less than 2,240 euros.
Since the amount incurred is less than the normal cost threshold, Mia cannot deduct these legal fees.
Example 2
Ralf and his wife are married and have 2 children. They have a taxable income of 90,000 euros and have been supporting Ralf's mother to the extent of 1,000 euros per month, or 12,000 euros per year.
Solution
1. Is it an extraordinary expense?
Yes, the support of needy relatives is a valid reason for the deduction of extraordinary expenses.
2. The threshold of normal load is determined as follows:
90,000 x 5% = 4,500 euros
The amount incurred by Ralf's household is above the normal load threshold, so the costs can be deducted.



